AI agents have become our daily companions, making our lives easier. From creating your grocery shopping lists to booking appointments, it has revolutionized the way we interact with machines. But what empowers them to generate human-like responses? The answer is Natural Language Processing, which can understand, interpret, and generate human language.
This blog discusses how NLP works in AI agents, including the key components, real-world applications, and benefits.
This blog covers:
Understanding AI agents
AI agents are intelligent systems designed to perceive their environment, make decisions, and take actions to achieve specific goals. It includes interconnected components that enable intelligent behavior in machines, such as Machine Learning, Neural Networks, Natural Language Processing (NLP), computer vision, and speech recognition.
Understanding Natural Language Processing
NLP is a branch of Artificial Intelligence (AI) that enables machines to understand, interpret, generate, and respond to human language in a meaningful manner. It helps bridge the gap between human communication and computer understanding.
Humans communicate using natural language, using speech, text, questions, and instructions. Computers, however, operate on structured data and programming languages. NLP enables machines to decode the unstructured, ambiguous, and context-rich language we use every day.
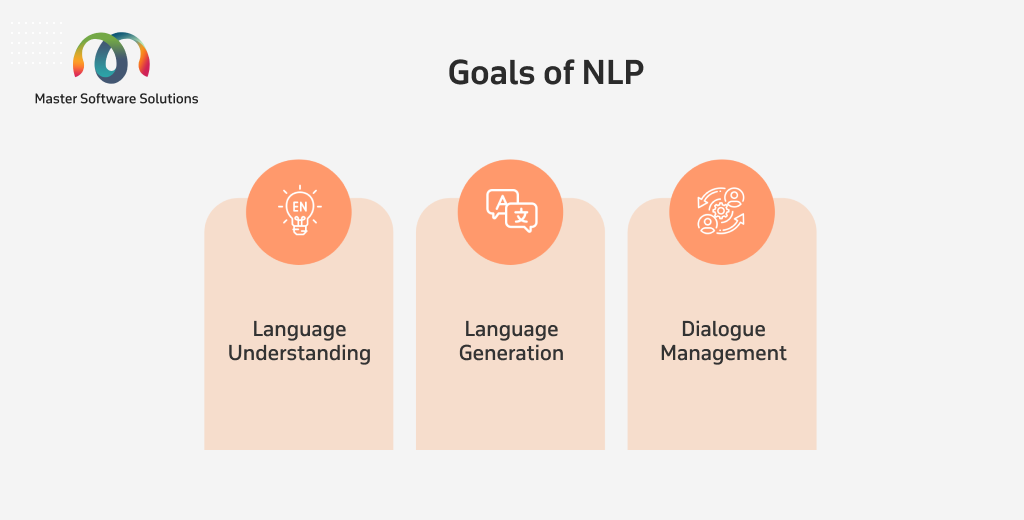
Goals of NLP
- Language understanding – Interpreting the meaning of the words, sentences, and context.
- Language generation – Producing human-like text or speech from data or structured input.
- Dialogue management – Handling back-and-forth conversations with context retention and intent recognition.
Common NLP tasks
- Tokenization – Breaking text into words or phrases (tokens).
- Part-of-speech tagging – Identify nouns, verbs, adjectives, etc..
- Named entity recognition (NER) – Detecting names, places, dates, etc..
- Sentiment analysis – Understanding emotional tone (positive, negative, neutral)
- Text classification – Categorizing text (spam vs. non-spam)
- Machine translation – Translating text from one language to another.
- Question answering – Finding answers from a given context.
- Text summarization – Generating short, relevant summaries from long documents.
Role of NLP in AI agents
- Allows AI to understand users’ queries and define their intent
- NLP enables the development of chatbots and virtual assistants to engage in human-like conversation.
- NLP can extract information from vast datasets for accurate answers.
- It enables agents to deliver personalized responses and recommendations tailored to each individual.
- It also enables agents to communicate in multiple languages.
Examples: AI chatbots for customer service, virtual assistants like Siri or Alexa, and content creation like GPT-4.
Benefits of NLP in AI agents
Natural Language Processing (NLP) in AI agents offers a range of powerful capabilities that can make interactions intelligent, human-like, and efficient. The benefits of NLP in AI agents are:
- Human-like understanding of language – NLP enables AI agents to understand natural human language, including slang, typos, or complex sentence structures. It allows conversational and intuitive interactions without requiring users to use rigid commands.
- Faster and scalable support – Agents can handle thousands of queries simultaneously, reducing wait times and improving user satisfaction. It automates tasks such as FAQs, appointment scheduling, or order tracking.
- Contextual and personalized responses – It enables agents to maintain context across conversations and customize responses based on user history or preferences.
- Multilingual communication – NLP can understand and respond in multiple languages, expanding accessibility and customer reach.
- Actionable insights from text data – NLP agents can analyze large volumes of unstructured text to derive insights and sentiments.
- Automation of repetitive tasks – It can automate tasks such as form filling, classification, summarization, and translation, saving time and cost.
- Consistency and accuracy – Unlike humans, NLP agents provide consistent responses without variation or fatigue, reducing human errors in high-stakes applications such as healthcare, finance, and legal.
- Cost reduction – It minimizes the need for large human support teams, enabling businesses to scale customer service, HR, and internal operations efficiently.
- Continuous learning and improvement – NLP-powered agents can learn from interactions, adapt to new language patterns, and improve over time.
Components of NLP in AI agents
Natural Language Processing (NLP) encompasses a wide range of subfields, broadly classified as natural language understanding (NLU) and natural language generation (NLG).
Natural Language Understanding
It focuses on enabling computers to understand user intent. NLU is the comprehensive engine of an AI agent, allowing it to understand the meaning, purpose, and context behind the user’s input. It includes
- Sentiment analysis
- Parsing/syntactic analysis
- Semantic analysis
- Named entity recognition (NER)
- Information extraction
Natural Language Generation
NLG enables the AI agents to generate clear, natural-sounding language as output from structured data or other input. It includes:
- Machine translation
- Text summarization
- Question answering
- Chatbots and virtual assistants
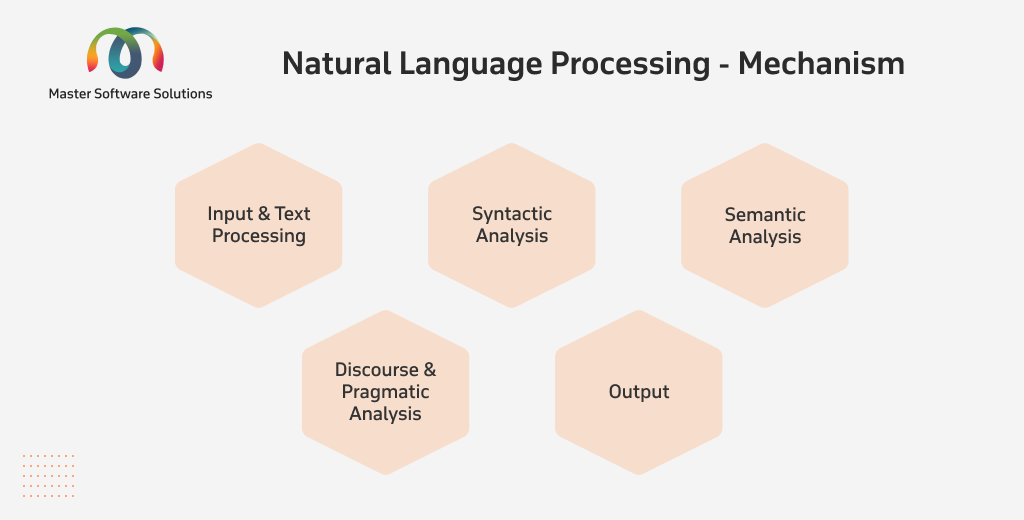
Natural Language Processing – Mechanism
Here is a breakdown of how NLP processes information and gives you the desired output:
Input and text processing
This is the raw data that users give to the system. The system breaks the text into simpler units known as Tokens. It converts everything into lowercase and reduces the words into their root form. Then, the words that do not carry much meaning are removed, such as “a,” “the,” and “is.”
Syntactic analysis
The system analyzes the grammatical structure of sentences to understand the relationship between the words. It identifies the role of each word (noun, verb, and adjective).
Semantic analysis
It determines the meaning of words, phrases, and sentences, including understanding context and relationships. It identifies the correct meaning of the words based on the context.
Discourse and pragmatic analysis
It understands how each sentence relates to the others within a larger text. The system considers the context and real-world knowledge to interpret the intended meaning.
Output
The system generates a result based on what is understood in human language.
Real-world applications of NLP in AI agents
Natural language processing (NLP) in AI agents is transforming how businesses and individuals are interacting with technology, enabling natural, human-like communication. Here are some use cases from real-world applications across industries.
Virtual assistance
AI agents such as Siri or Alexa use NLP to understand voice commands. It performs tasks, including setting reminders, playing music, or sending texts. Virtual assistants can answer general knowledge questions. They use speech recognition, detect intent, and generate a voice response.
Customer support chatbots
They are deployed on websites, mobile applications, and messaging platforms to answer FAQs, troubleshoot issues, and escalate complex queries to human agents. Example: “Where is my order?” Agent fetches the delivery status and replies in natural language.
E-commerce and retail
NLP can guide product searches with conversational filters, recommend items based on customer preference, and automate order tracking and returns, enhancing the shopping experience. Example: “Chatbot—’Looking for running shoes under $100?’ filters and displays results.
Healthcare virtual agents
These agents are implemented in telemedicine apps and hospital systems to schedule appointments, answer symptom-related questions, and provide plain-language explanations of lab results. Example: “I have a sore throat; what should I do?” The agent offers basic medical advice or referrals to specialists.
Logistics and supply chain
NLP AI agents for logistics and supply chain help manage delivery queries, track shipments, and resolve scheduling conflicts via conversational UI. Example: “When will my shipment #456 be delivered?” The agent provides real-time ETA.
Bottom-line
NLP technology has brought a paradigm shift along with artificial intelligence. It plays a foundational role in empowering AI agents to communicate, understand, and respond to humans in a way that feels natural and intuitive. This bridges the gap between human language and machine understanding. NLP enables AI agents to interpret intent, extract meaning, and generate personalized, context-aware responses. If you want to develop AI agents using natural language processing technology, we can help you. Schedule a meeting to discuss your business needs.