Is your ERP system driving growth or slowing your business?
In 2026, many organizations are still using legacy ERP systems that are costly to maintain, difficult to scale, and poorly integrated with modern technologies such as AI, cloud platforms, and advanced analytics. As business demands accelerate, these limitations become harder to ignore.
Ask yourself:
Can your current ERP adapt to changing business needs?
Do you have real-time visibility into your operations?
Is your system future-proof for compliance, security, and growth?
If your answer to all these questions is “No”, you are in the right place. Continue reading to find out how migrating to Odoo ERP can change your answer to “Yes.”
This article explores how to successfully migrate from a legacy ERP to Odoo ERP in 2026, covering readiness assessment, migration strategies, and key considerations to ensure a smooth transition and measurable ROI.
Table of Contents
Let’s start with understanding why legacy ERP systems are no longer fit for today’s business environment.
What is a legacy ERP system?
A legacy ERP system is an Enterprise Resource Planning solution that was implemented many years ago and is built on outdated technology architectures. These systems were typically designed for on-premise deployment, rigid business processes, and limited integration capabilities.
While legacy ERP platforms may still support core functions such as finance, inventory, or manufacturing, they often rely on:
- Obsolete programming languages or databases
- Heavy customizations that are difficult to modify
- Vendor-locked licensing and upgrade models
- Manual workflows and static reporting
Limitations of Legacy ERP in 2026
In 2026, a system is considered “legacy” not by its age, but by its inability to support modern business requirements, including scalability, automation, real-time analytics, and seamless digital integration. Here are the limitations of legacy ERP in 2026.
High operational and maintenance costs: Legacy ERP systems require expensive licenses, infrastructure, and specialized technical resources. Ongoing maintenance and upgrades often deliver minimal functional improvement while consuming significant budgets.
Limited scalability and flexibility: As businesses grow or evolve, legacy ERPs struggle to keep pace with the evolving market landscape. Adding new users, entities, or processes often involves complex customization and lengthy implementation cycles.
Poor integration with modern technologies: Most legacy systems were not built to integrate easily with cloud platforms, AI tools, mobile applications, or third-party software, resulting in data silos and manual workarounds.
Lack of real-time data and analytics: Reporting is often delayed, static, and dependent on manual data extraction, making it difficult for decision-makers to act quickly and accurately.
Security and compliance risks: Outdated architectures and limited vendor updates increase exposure to cybersecurity threats, making it harder to meet evolving regulatory requirements.
Insufficient user experience: Legacy ERP interfaces are complex and unintuitive, which lowers user adoption, increases training costs, and reduces productivity.
What is Odoo ERP software?
Odoo ERP software is a modern, modular Enterprise Resource Planning platform that integrates all core business functions into a single, unified system. Finance, sales, CRM, inventory, manufacturing, human resources, procurement, e-commerce, and other functions are integrated using a common database and consistent user experience.
Unlike legacy ERP systems, Odoo is built on a flexible, open-source architecture. Organizations can start with the modules they need and expand over time. Odoo supports cloud, on-premise, and hybrid deployments, making it suitable for businesses of all sizes and industries.
Why is Odoo ERP a strategic choice in 2026?
In 2026, Odoo is widely recognized not only as an ERP system but also as a business management platform that enables automation, real-time visibility, and rapid adaptation to change. Here are the reasons to choose Odoo ERP in 2026.
Modular and scalable by design: Odoo enables businesses to implement ERP incrementally. They can also add new modules, users, and workflows as requirements evolve, supporting long-term growth without disruption.
Cost-effective ERP alternative: Compared to legacy ERP vendors, Odoo offers significantly lower licensing and implementation costs, with predictable pricing and reduced dependency on proprietary technology.
Native cloud and AI readiness: Odoo is built to integrate with cloud infrastructure, AI-driven automation, and advanced analytics, capabilities that are increasingly critical for competitive advantage in 2026.
Strong integration capabilities: Through APIs and a rich app ecosystem, Odoo integrates seamlessly with third-party applications, eliminating data silos and manual processes.
Enhanced user experience and adoption: Odoo’s modern, intuitive interface reduces training time and improves user adoption, leading to higher productivity across departments.
Open-source flexibility with enterprise support: Businesses benefit from open-source customization and transparency along with regular updates, enterprise-grade support, and a global partner network.
Open-source flexibility with enterprise support: Businesses benefit from open-source customization and transparency along with regular updates, enterprise-grade support, and a global partner network.
Also Read: Reasons to Migrate to the Latest Version of Odoo in 2026
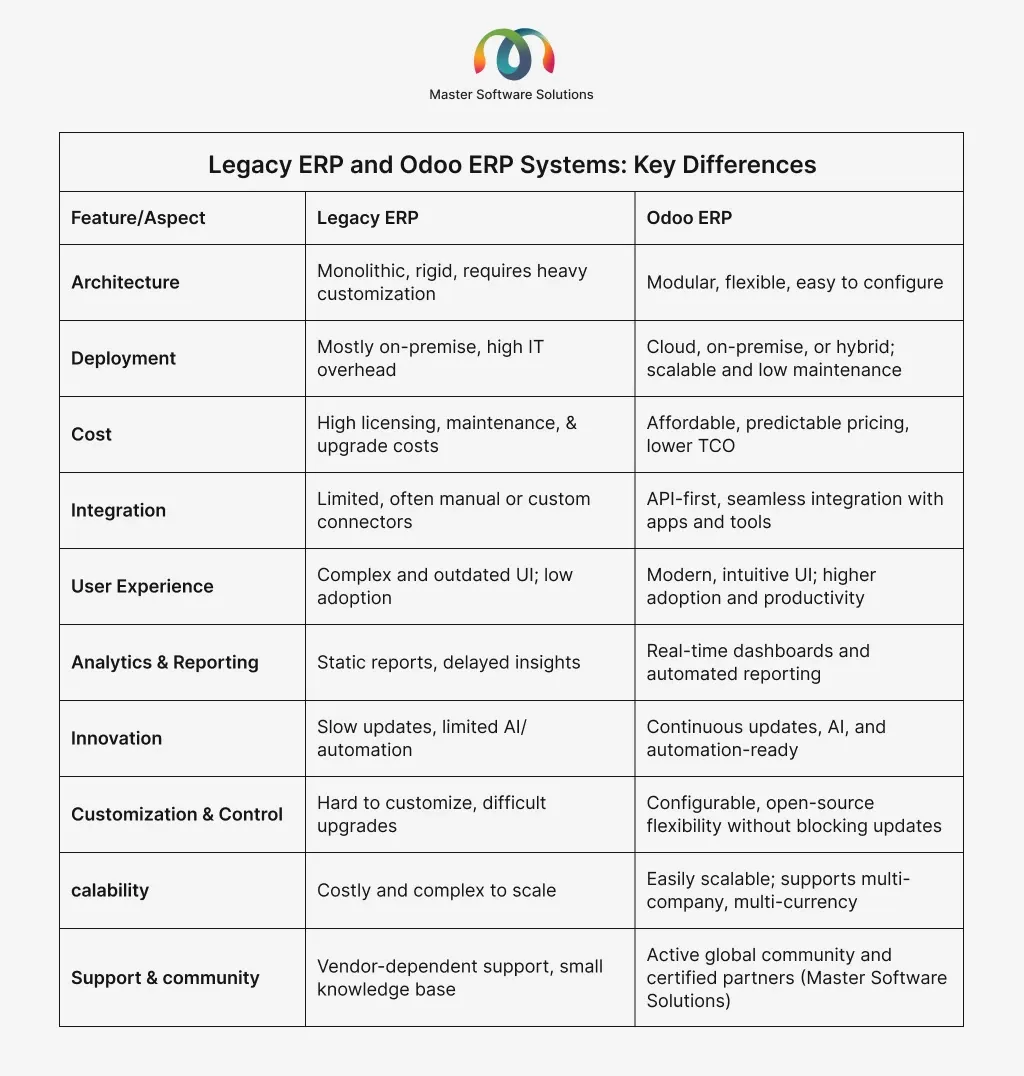
Legacy ERP and Odoo ERP systems: key differences
Key business drivers for migrating to Odoo ERP software in 2026
Legacy ERP systems often struggle to keep up with evolving operational, technological, and market demands in the changing business environment. Organizations are increasingly looking for modern ERP solutions that deliver efficiency, flexibility, and actionable insights. Here are the primary business drivers that are motivating companies to migrate to Odoo ERP in 2026.
Operational efficiency and process standardization
Odoo ERP streamlines workflows across finance, inventory, sales, manufacturing, and HR. Automating repetitive tasks reduces errors, saves time, and ensures consistent processes across departments.
Real-time data visibility and reporting
Legacy ERP systems often provide delayed or siloed data. Odoo offers real-time dashboards, reporting, and analytics, empowering leaders to make faster, informed decisions.
Enhanced customer experience
With integrated CRM, sales, and e-commerce modules, Odoo enables businesses to manage leads, orders, and customer interactions in a unified system, improving responsiveness and satisfaction.
Support for remote and global operations
Cloud and hybrid deployment options enable distributed teams to access the system securely from anywhere. Multi-company, multi-currency, and multi-language support simplified global operations.
Faster innovation and adaptability
Odoo’s modular and open-source architecture enables organizations to implement new modules, adopt AI-driven automation, and adjust workflows, keeping pace with changing business needs.
Cost efficiency
Lower licensing, implementation, and maintenance costs compared to legacy ERP systems free up budgets for strategic initiatives, while reducing reliance on specialized IT resources.
Compliance and security
Odoo provides robust access controls, audit trails, and automated compliance features, enabling organizations to meet regulatory requirements and maintain data security.
Migration strategy: Legacy ERP to Odoo
Migrating from a legacy ERP system to Odoo ERP is crucial for modernizing operations, boosting efficiency, and remaining competitive in 2026. A structured migration strategy ensures minimal disruption, reduced risk, and maximized value of the new ERP system. Here are a few migration strategies to consider when migrating to the Odoo ERP system.
Assess current systems and define objectives
Before beginning any migration, organizations must assess the performance and limitations of their ERP system. This involves analyzing current workflows, identifying pain points, and understanding compliance or regulatory requirements. It is crucial to set specific goals for the business, such as increasing automation, cutting expenses, improving data visibility, and improving customer satisfaction. Defining these goals upfront ensures the migration aligns with the long-term business strategy.
Choose the migration approach
Choosing the best migration strategy is crucial to striking a balance between risk and speed. A big-bang migration involves moving all modules and functions to Odoo simultaneously, offering faster implementation but carrying a higher risk of downtime or disruption. A phased migration, on the other hand, transitions one module or department at a time, reducing risk and easing user adoption, though it takes longer to complete. The choice depends on organizational complexity, readiness, and risk tolerance.
Data migration planning and validation
Businesses need to inventory all data from the legacy system, including master data (including customers, vendors, and products) and transactional records (orders, invoices, and inventory). Data should be cleansed to remove duplicates, standardize formats, and correct errors. Proper mapping of legacy fields to Odoo modules is necessary to maintain compatibility. After migration, thorough validation ensures that data integrity is preserved and workflows function correctly.
Customization vs. configuration
During migration, organizations must decide between customizing Odoo to replicate legacy features and using built-in configuration options. Minimizing custom code is recommended to reduce complexity and simplify future upgrades. Odoo’s modular and flexible architecture achieves business requirements through configuration, enabling faster deployment while maintaining scalability.
Integration with existing systems
Many businesses rely on additional software systems such as CRMs, e-commerce platforms, or logistics tools. Effective migration requires planning for seamless integration between Odoo and these third-party systems. Using Odoo’s native integration tools or APIs ensures data flows smoothly, prevents silos, and maintains continuity of business processes after migration.
Infrastructure and deployment planning
Deciding where and how to deploy Odoo is crucial for performance and scalability. Organizations can choose between cloud, on-premise, and hybrid deployments based on their security, accessibility, and growth needs. To maintain uptime and reliability, proper infrastructure planning includes ensuring sufficient capacity for increased transaction volumes, as well as implementing backups, disaster recovery, and monitoring systems.
Testing and validation
Before going live, rigorous testing is required to ensure that Odoo meets business requirements. Unit tests, system tests, and user acceptance tests (UAT) should confirm that all workflows, modules, and integrations function correctly. Testing also helps identify potential issues early, reducing the risk of operational disruptions while going live.
Go-live and post-migration support
A successful migration concludes with careful execution of the go-live plan. This includes minimizing downtime, providing user training, and ensuring documentation is available. Post-migration support and monitoring are critical to quickly address any issues, optimize system performance, and ensure smooth adoption across the organization.
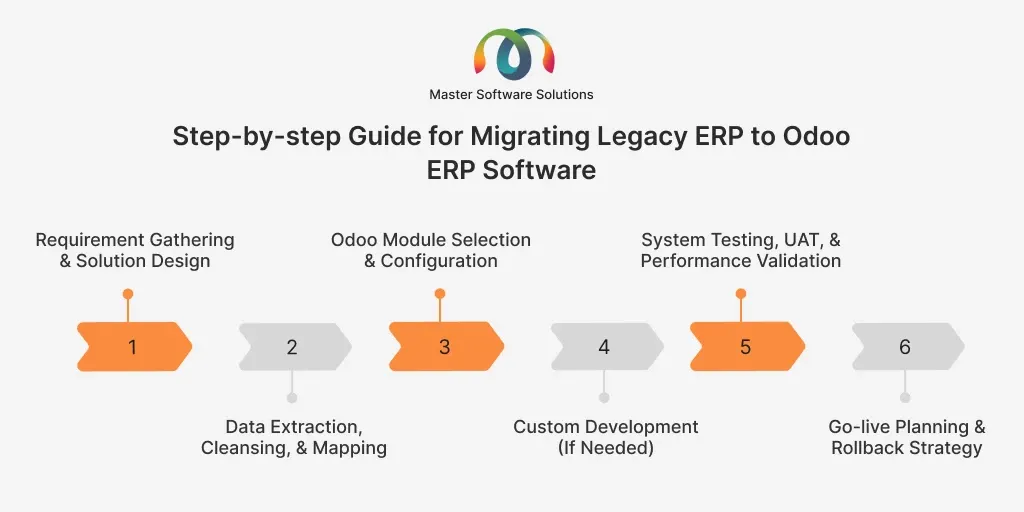
Legacy ERP to Odoo ERP migration: step-by-step guide
A structured, step-by-step migration process is essential to ensure a smooth transition from a legacy ERP system to Odoo. Each phase focuses on minimizing risk, maintaining business continuity, and ensuring the new system aligns with operational and strategic goals. Here is a step-by-step guide for migrating legacy ERP to Odoo ERP software.
Requirement gathering and solution design
This phase involves understanding current business processes, pain points, and future requirements. Stakeholders collaborate to define functional and technical needs. Based on this analysis, a tailored Odoo solution design is created to align with business objectives.
Data extraction, cleansing, and mapping
Data is extracted from the legacy ERP system and reviewed for accuracy and relevance. Cleansing removes duplicates, errors, and outdated records. Clean data is then mapped to Odoo’s data structure to ensure consistency and reliability.
Odoo module selection and configuration
Relevant Odoo modules are selected based on business requirements. Each module is configured to match workflows, roles, and reporting needs. This configuration-driven approach reduces the need for heavy customization.
Custom development (if needed)
Custom development is performed only when standard Odoo features cannot meet specific business needs. This may include custom reports, integrations, or workflows. The goal is to keep customization minimal to ensure easier upgrades and maintenance.
System testing, UAT, and performance validation
Comprehensive testing ensures the system works as intended. User Acceptance Testing (UAT) validates real-world business scenarios, while performance testing confirms system stability, speed, and data accuracy before launch.
Go-live planning and rollback strategy
A detailed go-live plan ensures minimal downtime during the transition. Backup and rollback strategies are prepared in case issues arise. Monitoring changes after migration helps stabilize the system and support users during the initial adoption.
Common migration challenges and how to avoid them
Migrating from a legacy ERP system to Odoo ERP comes with risks if not managed carefully. Understanding common migration challenges in advance enables organizations to plan mitigation strategies, minimize disruption, and ensure a successful ERP transition in 2026. Here are the common challenges faced during Odoo ERP migration.
Data loss or inconsistency risks
Poor data quality, incorrect mapping, or incomplete transfers can result in missing or inaccurate data. This can disrupt reporting and daily operations. Mitigation involves thorough data cleansing, validation, test migrations, and reconciliation before going live.
User resistance & adoption issues
Employees may resist change due to unfamiliar processes or fear of productivity loss. Low adoption can reduce the value of the new ERP system. Early user involvement, role-based training, and clear communication about benefits help drive acceptance and engagement.
Downtime and business continuity concerns
ERP migration can temporarily disrupt operations if not carefully planned, resulting in unexpected downtime and impacting customers and revenue. A phased migration approach, detailed cutover planning, and fallback strategies help ensure business continuity.
Scope creep and budget overruns
Uncontrolled changes in requirements during migration can maximize costs and delay timelines. This often occurs due to unclear objectives or excessive customization. Defining scope early, prioritizing requirements, and enforcing change control processes mitigate this risk.
Security and compliance considerations
Data migration exposes sensitive business information to potential security and compliance risks. Inadequate access controls or outdated policies can lead to violations. Implementing role-based access, encryption, audit trails, and compliance checks ensures data security during the migration process.
Cost, ROI, and timeline expectations in 2026
Migrating from a legacy ERP to Odoo in 2026 is a strategic investment that balances cost efficiency with long-term business value. Understanding the financial and time implications helps organizations plan realistic and successful ERP transformations.
Cost
Migration costs typically include licensing, implementation, data migration, integrations, training, and support. Compared to traditional ERP systems, Odoo offers a lower total cost of ownership due to flexible pricing and reduced infrastructure requirements.
ROI
Organizations benefit from improved efficiency, automation, real-time monitoring, real-time reporting, and lower maintenance costs. Most businesses see a tangible return on investment within 6-18 months, depending on the scope of implementation and user adoption.
Timeline
Implementation timelines vary by complexity. Small to mid-sized projects usually take 3-6 months, while larger, multi-module deployments may require 6-12 months.
Conclusion
As businesses move deeper into a digital-first economy, legacy ERP systems are becoming a barrier to efficiency, scalability, and innovation. Migrating to Odoo 2026 is an excellent way to gain real-time visibility, lower operational costs, and lay a flexible foundation for future growth.
Master Software Solutions helps organizations navigate this journey with confidence. From ERP assessment and migration planning to implementation, customization, and post-go-live support, our team ensures a smooth transition from legacy systems to Odoo, minimizing risk while maximizing ROI. Contact us today for a personalized Odoo ERP consultation and discover how we can help transform your operations in 2026 and beyond.