Do you feel stuck in the slow lane while the competition races ahead? Well! You are not alone. Staying ahead in the ever-evolving market means minimizing costs and improving efficiency, which can only be achieved with the adoption of technology.
With so many options available, it’s easy to get lost and end up with a system that doesn’t even fit your business. This is why understanding the difference between traditional automation and AI agents is essential. Traditional automation is like a normal car that can get you from one place to another. On the contrary, AI agents are like self-driving cars that learn about the roads and adapt to traffic, making driving decisions and taking actions.
Do you know that “Fifty-one percent of businesses have begun exploring the use of AI agents, with 37% already utilizing them?” Are you one of them? If not. This is the right time for you to start exploring and implementing one.
This guide explains the key differences between traditional automation and AI agents, helping you select the best technology for your business.
The blog covers
What is traditional automation?
Traditional automation relies on predefined rules, scripts, or workflows to complete repetitive and structured tasks without human intervention. It follows an “if-this-then-that” logic, which means that it executes tasks based on fixed conditions and sequences. Traditional automation tools such as Robotic Process Automation (RPA), machine learning, and natural language processing are used to initiate a predefined workflow. While they are effective for predictions and repetitive tasks, traditional automation struggles with unstructured data or decision-making in dynamic environments, where AI agents excel.
Characteristics of traditional automation
- Rule-based processes – Actions based on predefined programming instructions.
- No learning capabilities – It can not adapt or improve, unless preprogrammed manually.
- Structured data reliance – Works best with consistent, well-defined inputs.
- Limited flexibility – Changes in process or environment require manual updates to the automation logic.
Example
Setting thresholds in inventory management can trigger the purchase orders. Suppose you want your system to automatically place purchase orders to ensure that you never run out of stock. You can configure your ERP to enable you to set a minimum threshold for your inventory. If you have set the value to be 50, this means that the system will initiate a purchase order when your inventory count hits 50.
Benefits of traditional automation
Traditional automation offers several advantages for businesses dealing with repetitive, rule-based tasks. Here are the benefits of conventional automation:
Consistency
It delivers uniform results every time a task is executed. As it follows predefined rules and logic, it eliminates the variability and errors associated with manual processes. This ensures reliable output quality, making it ideal for industries that need precision and standardization.
Scalability
Automated processes handle larger workloads easily without proportionally increasing costs or manpower. Whether it is processing thousands of transactions or managing large volumes of data, traditional automation can expand operations efficiently as business demands grow.
Cost-effectiveness
It reduces manual labor, minimizes errors, and accelerates task completion, leading to significant cost savings over time. It is cost-effective for repetitive and rule-based processes where ROI is quickly realized through reduced operational expenses and improved productivity.
Limitations of traditional automation
Traditional automation comes with several limitations that restrict its effectiveness in dynamic or complex environments. Here are the key drawbacks.
Rigid framework
Traditional automation relies on predefined rules and scripts. Any change in the input, process, or environment causes the automation to fail and requires manual reprogramming.
Limited problem-solving
It is only ideal for repetitive or rule-based tasks. Traditional automation falls short for processes that involve creativity, problem-solving, or contextual understanding.
High maintenance over time
As processes evolve or business rules change, manual updates can make maintaining traditional automation time-consuming and costly.
What are AI agents?
AI agents are intelligent software systems designed to perceive their environment and take actions autonomously to achieve specific goals. Unlike traditional automation, which follows rigid, rule-based logic, AI agents use machine learning, natural language processing, and other AI technologies to adapt, learning, and respond dynamically to changing conditions and inputs.
Characteristics of AI agents
- Autonomous decision-making – They can analyze data, assess situations, and make decisions without human intervention.
- Learning and adaptation – They learn from new data, feedback, or experience using machine learning algorithms to improve over time.
- Context awareness – AI agents understand and interpret context, such as user intent, environment, or past interactions, to act more intelligently and smartly.
- Interaction capabilities – They can interact with users, systems, or other agents using natural language or APIs, enabling more human-like or collaborative behavior.
- Goal-oriented behavior – They are designed to pursue objectives, whether it is optimizing supply chain routes, automating customer service, or managing IT operations.
Example: AI agents for inventory and demand planning
- They continuously collect data from multiple sources (sales, market trends, supplier information, weather, or social media), building a comprehensive view of supply and demand.
- Using ML models, they predict future demand with accuracy. They identify patterns, seasonality, and emerging trends.
- Based on forecasted demand, they adjust inventory levels by reordering products when needed.
- Respond to unexpected changes, such as supply delays or sudden demand spikes, by updating plans and making recommendations accordingly.
- They simulate “what-if” scenarios to prepare for uncertainties (supply disruptions or policy changes) and recommend the best course of action.
Benefits of AI agents
AI agents provide numerous benefits, including the transformation of your business operations, increased efficiency and productivity, and cost savings. The advantages of AI agents are:
Autonomous decision-making
AI agents can operate without constant human input. They can assess data, understand context, and make decisions, allowing for faster and more efficient operations.
Improved user experience
They understand user intent, provide personalized responses, and deliver instant support across platforms. Whether assisting customers or automating internal service requests, they can create smoother, faster, and more satisfying experiences.
Enhanced operational efficiency
AI agents help streamline operations, reducing redundancies, minimizing errors, and speeding up task execution. This can lead to increased productivity and cost savings across departments.
Learning and adaptability
Unlike static automation tools, AI agents learn from new data and past outcomes. This enables them to adapt to changing conditions, improving their performance over time and staying effective in dynamic business environments.
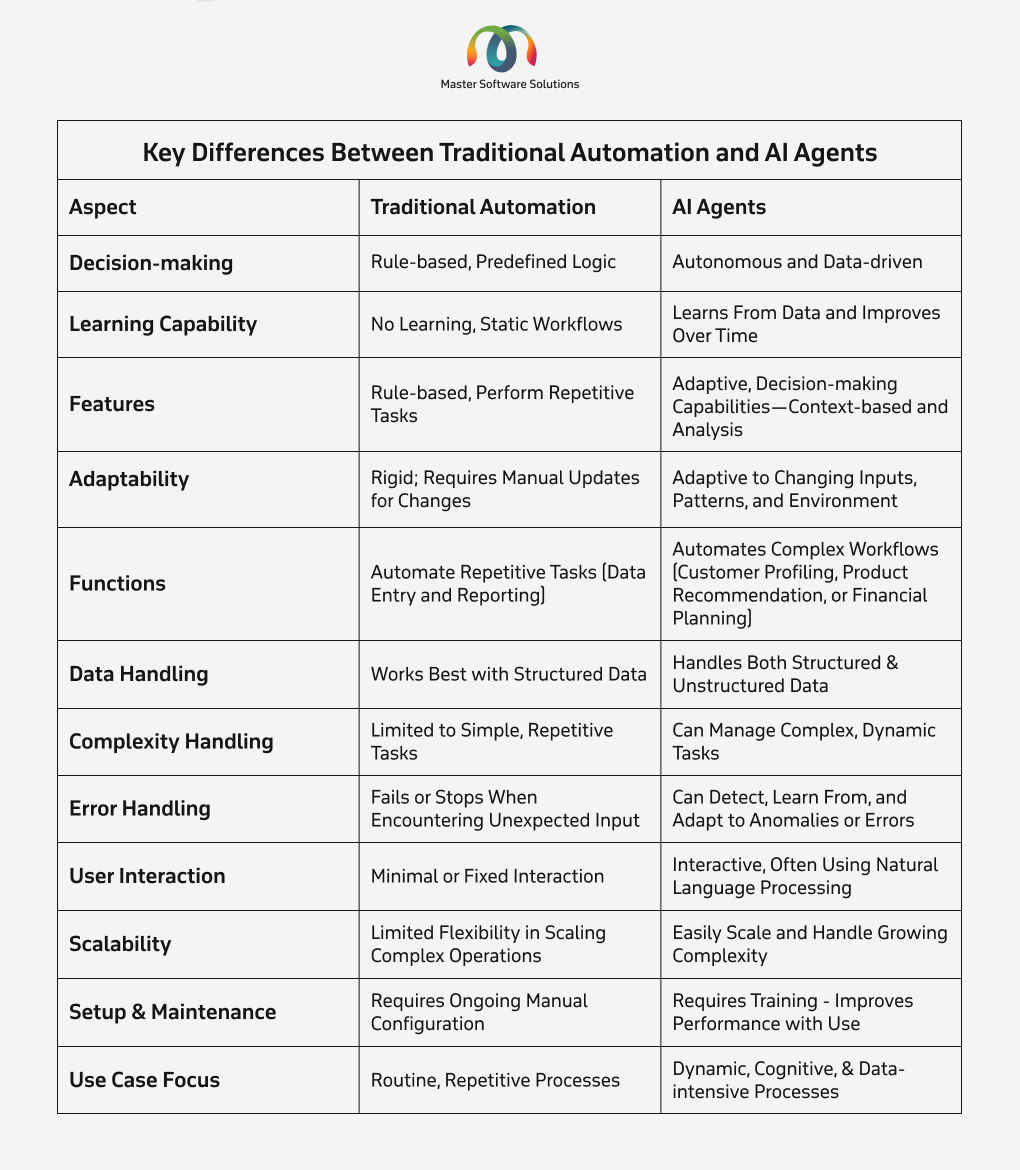
Key differences between traditional automation and AI agents
Use case: conventional automation vs. AI agents
Here we will understand the difference with a real-world example.
Scenario – Inventory Reordering
With traditional automation
A rule-based system is set up with fixed thresholds. The Rule – If the stock level falls below 40 units, trigger a reorder of 500 units for that product. This works great during normal operations but fails to adapt to changing demand patterns, including seasonal spikes or sudden bulk orders from offices. It can not prioritize reorders based on supplier lead times, upcoming holidays, or promotional campaigns. Any change in the demand pattern requires a manual update to rules or reorder points.
This system is ideal for repetitive and predictable inventory flows. However, it lacks flexibility, which leads to overstocking during low demand or stockouts during unexpected surges.
With AI agents
An AI-powered inventory agent constantly monitors sales data, historical data, weather forecasts, customer behavior, and even the event calendar. It uses machine learning models to forecast demand for the coming week. It can dynamically adjust reorder quantities based on trends, supplier lead times, delivery delays, and warehouse capacity. If it notices a demand spike (due to seasonality in the beverage or clothing industry), it promptly increases reordering quantity when the stock is too low.
An AI agent ensures just-in-time inventory, reduces costs, prevents stockouts, and adapts to changes without manual intervention.
Which is right for your business?
It is crucial to choose the right tool between AI agents and traditional automation to ensure you meet your business goals. Here is the breakdown of when each works best.
When should you choose traditional automation?
It is the right choice when your business processes are stable, repetitive, and rule-based. It delivers consistent performance without the complexity or cost of advanced AI systems. You can choose traditional automation when:
- Your business processes are predictable and unchanging
- Data is structured
- Repetitive and time-consuming tasks that do not need judgment or learning
- You need complete control over your decisions
When should you choose AI agents?
AI agents are best suited for dynamic, data-driven, and decision-heavy processes that require more than just rule-following. You should use AI agents when your company requires intelligence, adaptability, and the ability to learn from updated data. You can choose traditional automation when:
- Processes involve complex or changing variables.
- It is critical to make real-time decisions.
- Data is unstructured.
- You need learning and adaptability.
- Scalability with intelligence is needed.
Final thoughts
Businesses must choose the right tools to drive efficiency and productivity. Traditional automation is ideal for repetitive or rule-based tasks, while AI agents can work dynamically and adapt to evolving conditions. You can choose the right tool based on your business requirements.
Master Software Solutions is an IT-based service provider that provides digital transformation services. We offer AI business process and consultation services, including AI chatbot development, Robotic Process Automation, workflow automation, and business process automation. Our automation team is proficient in using OpenAI, UiPath, and MS Power Automate to ensure that you achieve higher automation, better decision-making, and seamless workflows.
We also provide AI agent development services, including consultation, agent development, interactions, training & optimization, behavioral modeling, and deployment and scalability. With extensive knowledge and skills in working with LLMs (GPT, Gemini, Dall-E, Gemma, etc.), machine learning, and NLP, our team has also built turnkey AI solutions that you can explore. To learn more about how we can help your business, book a consultation.