It is essential to have the right enterprise resource planning system in this competitive market landscape. However, with so many ERP system options available, ranging from cloud-based platforms to industry-specific solutions, selecting the right one can be challenging. Each type of ERP is designed to meet different operational needs, deployment preferences, and business sizes.
Regardless of your business or industry type, understanding the types of ERP solutions is the first step towards making an informed decision. This blog examines various ERP types based on deployment, business size, architecture, and licensing models to help you determine which is best for your goals and growth strategy.
The blog covers:
ERP systems by deployment options
When selecting an ERP system, choosing the deployment method is an important decision. The deployment model can impact cost, scalability, maintenance, and cost control. Choosing the right deployment model determines how your system will be managed, its accessibility, and the resources needed to keep it running smoothly. Major ERP deployment options are:
On-premise ERP
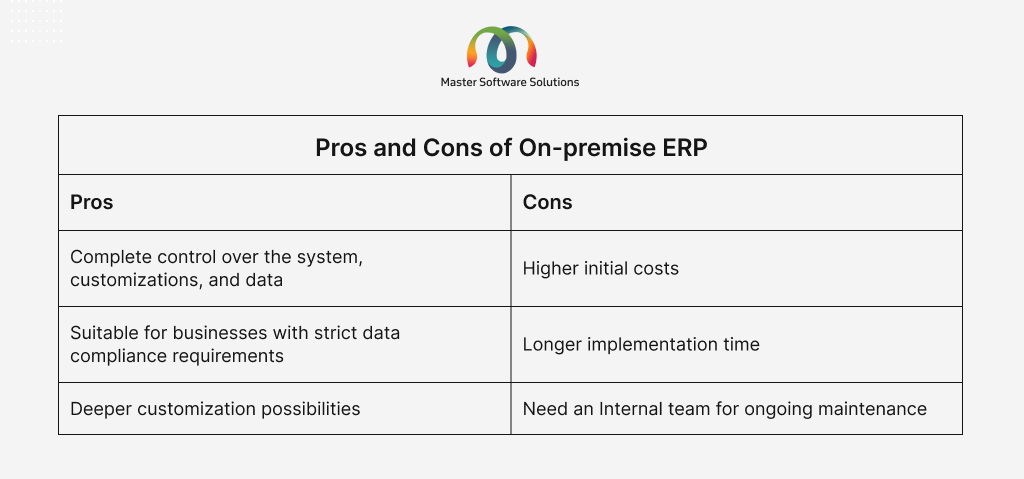
An on-premise ERP is installed on the company’s server and infrastructure. The organization is responsible for maintaining the hardware, performing updates, managing data backups, and ensuring the security of the system. The features of on-premise ERP are:
- It is hosted entirely within your organization
- You have complete ownership of the software and data
- It is highly customizable and can fit your complex and unique business processes
On-premise ERP is suitable for larger enterprises, regulated industries, or businesses that already have an IT infrastructure.
Cloud ERP
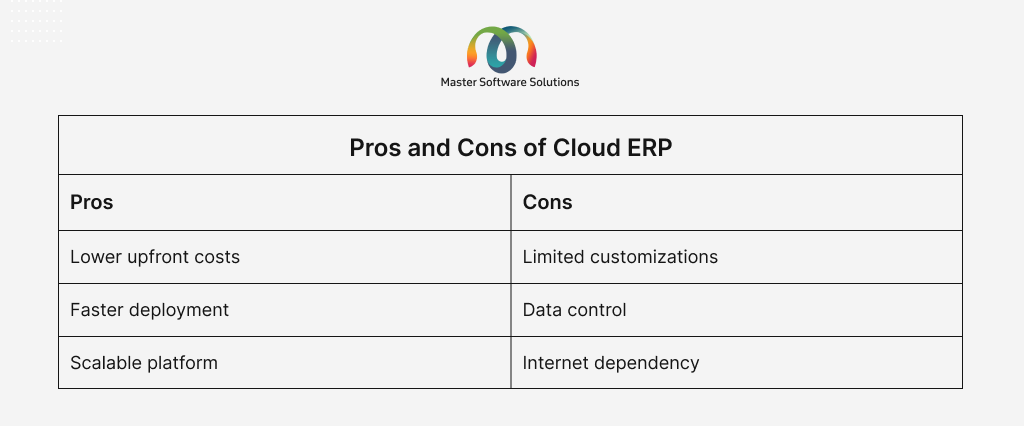
A cloud ERP is hosted by the software vendor or a third-party cloud provider and accessed via a web browser. It follows a subscription pricing model and is referred to as Software-as-a-Service (SaaS). The key features of Cloud ERP:
- It is hosted on the vendor’s infrastructure or a third-party cloud provider, such as AWS or Google Cloud.
- You can access cloud ERP solutions remotely through the internet.
- It includes automatic updates and data backups.
A cloud-based ERP is ideal for start-ups, small- to medium-sized businesses with remote teams, and those seeking low maintenance and rapid deployment.
Hybrid ERP
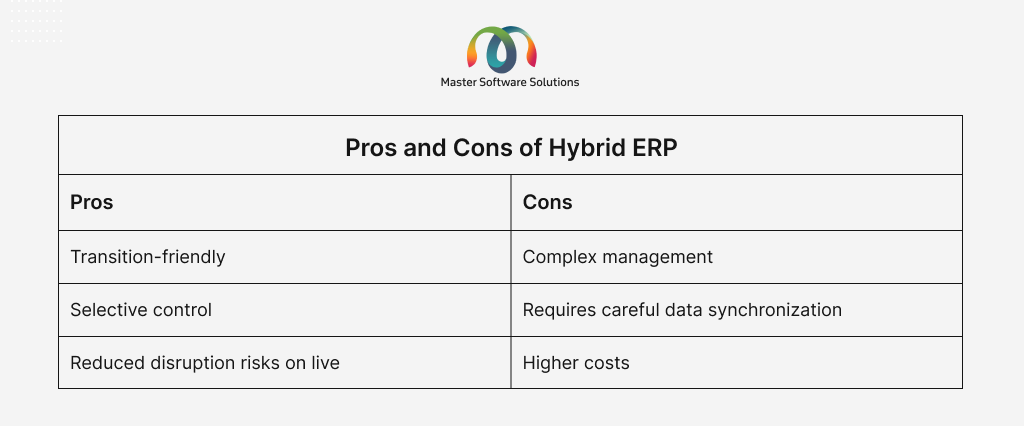
A hybrid ERP is a mix of both on-premise and cloud-based components. For instance, the core financials might run on-premise, while CRM and reporting tools are cloud-based. The key features of a hybrid ERP are:
- Combine the benefits of both models.
- Allows gradual cloud adoption without disrupting existing systems
- Flexibility in data hosting and access
Hybrid ERP is best for businesses with complex operations that are currently using legacy systems, or when specific departments are cloud-ready while others are not.
Industry-focused ERP
“Industry-focused ERP” is a broad term that refers to both industry-specific and vertically optimised general ERPs. It refers to any ERP system that targets a specific industry, regardless of whether it is fully built or tailored through extensions. Examples include Microsoft Dynamics 365, Odoo, and SAPS/4HANA. It is suitable for vendors serving multiple industries with sector-based editions.
General-purpose ERP
A general-purpose ERP system is designed to serve a wide range of industries. It includes standard modules such as finance, human resources, inventory, sales, procurement, and CRM. The features of the general-purpose ERP are:
- It is a broader and more adaptable platform.
- Offers extensive customization scope.
- It offers a modular approach that fits different business types.
The general-purpose ERP is ideal for non-specialized industries or those with unique operations that require a flexible system. Examples of general-purpose ERPs include SAP Business One, Oracle NetSuite, and Microsoft Dynamics 365.
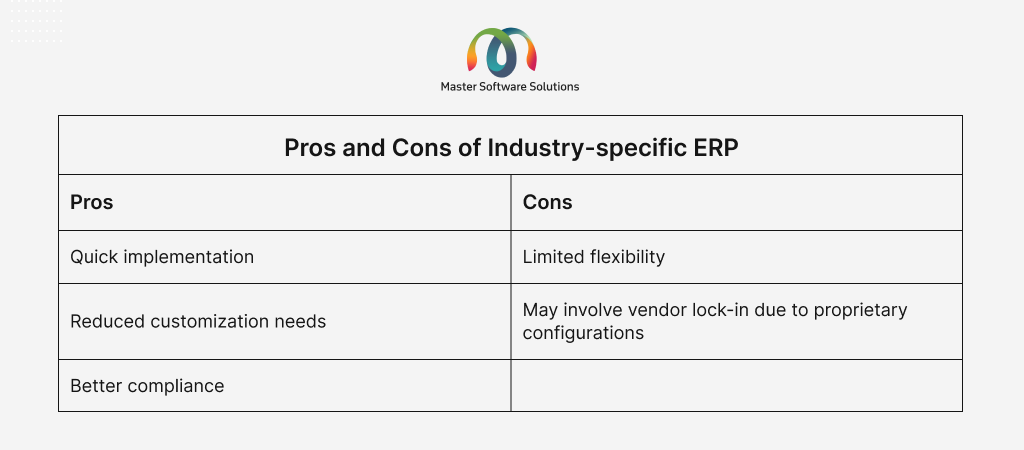
Industry-specific ERP
An industry-specific ERP system is purpose-built for a particular industry, such as manufacturing, food and beverage, coffee, bottled water, and dairy. The key features of industry-specific ERP are:
- Pre-built modules tailored for specific workflows.
- Industry-focused terminology and compliance tools.
- Configured for faster implementation in niche verticals.
Industry-specific ERP systems are best for companies in industries with standardized processes, strict regulations, or operational complexities that require a specialized approach. Examples: Odoo Manufacturing, Epicor ERP, Retail Pro, etc..
Based on business size
The size of your business plays a crucial role in choosing the right ERP system. Each category, whether you are a small startup or a multinational enterprise, has unique needs in terms of features, scalability, cost, and implementation complexity. ERP systems are often built with these distinctions in mind to ensure the right level of functionality, flexibility, and performance.
Small business ERP
Small business ERPs are lightweight, cost-effective systems designed for startups or small businesses with limited resources and relatively simple business processes. The key features of small business ERP are:
- Easy to use with minimal technical expertise required.
- Core module only.
- Cloud-based deployment is common.
- Minimal customization required.
It is best for startups, micro-enterprises, and small businesses with fewer than 50 employees or operational needs. Examples include Zoho ERP, Odoo (Community Edition), QuickBooks Enterprise, and ERPNext.
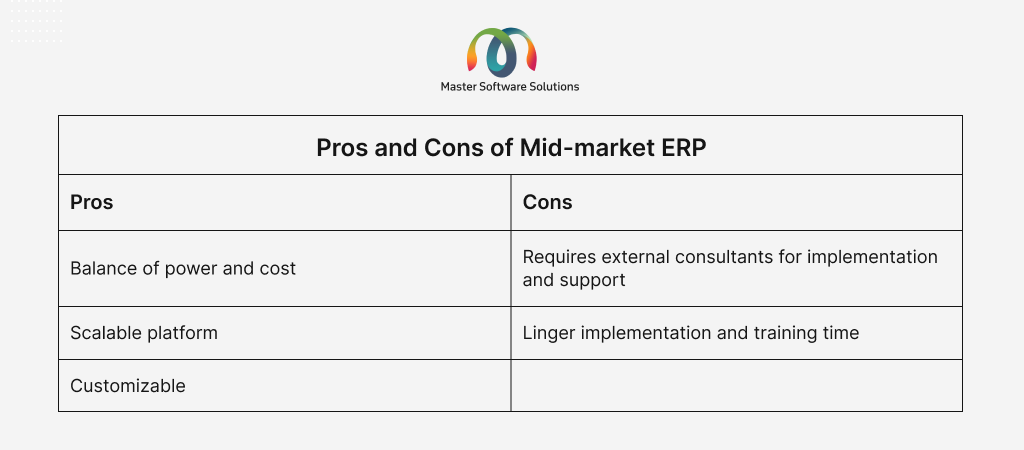
Mid-market ERP
The mid-market ERP serves growing businesses that have more complex operations and require better integration, reporting, and scalability. Features of mid-market ERP are:
- Modular structure with flexibility to add features as your business grows.
- Can handle multi-location, multi-currency, and multi-entity setups.
- Offers integrations with third-party systems (CRM, e-commerce)
This ERP type is suitable for growing businesses with 50-500 employees, or those operating in multiple regions or product lines. Examples include Odoo (Enterprise Edition), Microsoft Dynamics 365 Business Central, SAP Business One, and Acumatica.
Enterprise ERP
Enterprise ERPs are large-scale systems designed for global corporations and large enterprises with complex, high-volume operations. The key features of enterprise ERP are:
- It consists of advanced modules like supply chain planning, warehouse automation, BI, compliance, and governance.
- It can handle high transaction volumes, larger user bases, and multiple business units.
- The system offers a high degree of customization and security features.
The enterprise ERP is suitable for enterprises with over 500+ employees, multiple subsidiaries, or international operations. Examples include SAP S/4HANA, Oracle, Microsoft Dynamics 365 Finance & Operations, and Infor CloudSuite.
Based on ERP architecture
ERP systems are built on different architectural models that determine how their components interact, how easily they can scale or upscale, and how flexible they are for customization. The two most common architectural types are Modular ERP and Monolithic ERP. Understanding the difference between them helps businesses select a system that matches their growth plan, operational complexity, and integration needs.
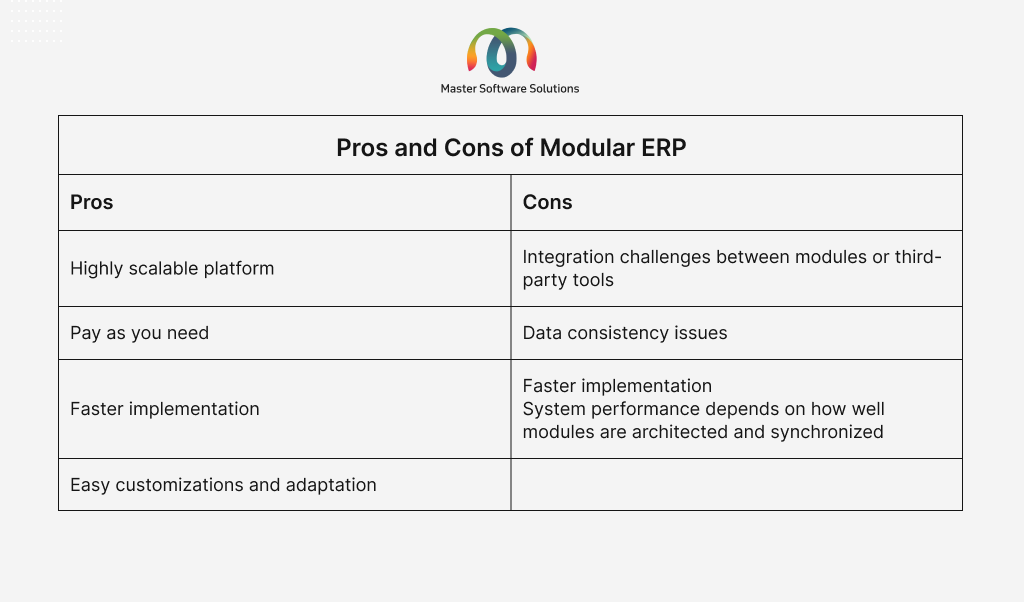
Modular ERP
Modular ERP systems are composed of independent but integrated modules, each representing a specific business function, such as finance, HR, inventory, CRM, or manufacturing. Businesses can pick and implement the modules that match their current need and add more as they grow. The features of Modular ERP are:
- Built using a component-based approach.
- Each module can be added, removed, or upgraded independently.
- These ERP solutions are often cloud-based or hybrid in nature.
Modular ERPs are ideal for SMEs, startups, and growing businesses that want to implement ERP gradually or have changing operational requirements. Examples are Odoo, ERPNext, and Microsoft Dynamics 365.
Monolithic ERP
A monolithic ERP is a single, unified system where all the modules are tightly integrated and built in a shared codebase. All functions, including finance, sales, inventory, and HR, are part of a large platform with a centralized database. The key features of monolithic ERP are:
- Everything is interconnected in a single software solution.
- It provides a consistent user interface and shared data model across all functions.
- The monolithic ERP is typically deployed on-premise or in a private cloud.
Monolithic ERPs are ideal for large enterprises that have standardized and organization-wide processes, requiring full system integration and control. Examples include SAP S/4HANA, Oracle ERP Cloud, and Infor CloudSuite.
Based on the licensing model
ERP systems are also classified based on their licensing and distribution. This can impact your costs of ownership, customization rights, and vendor dependency. There are two major types—open-source ERP and proprietary (paid) ERP.
Open-source ERP
Open-source ERP provides access to source code, allowing businesses to modify, customize, and extend the software to meet their needs. These systems are often free under open-source licenses, and companies may pay for hosting, support, or professional services. Features of an open-source ERP are:
- Free or low-cost software licensing.
- The ERP system’s source code is open for modifications.
- These systems have strong community-driven development.
- They are usually modular and flexible.
Open-source ERP systems are ideal for startups, SMBs, or tech-savvy businesses with in-house IT teams or a need for custom features at a low cost. These ERPs are Odoo (Community Edition), ERPNext, Dolibarr, Tryton, and Metasfresh.
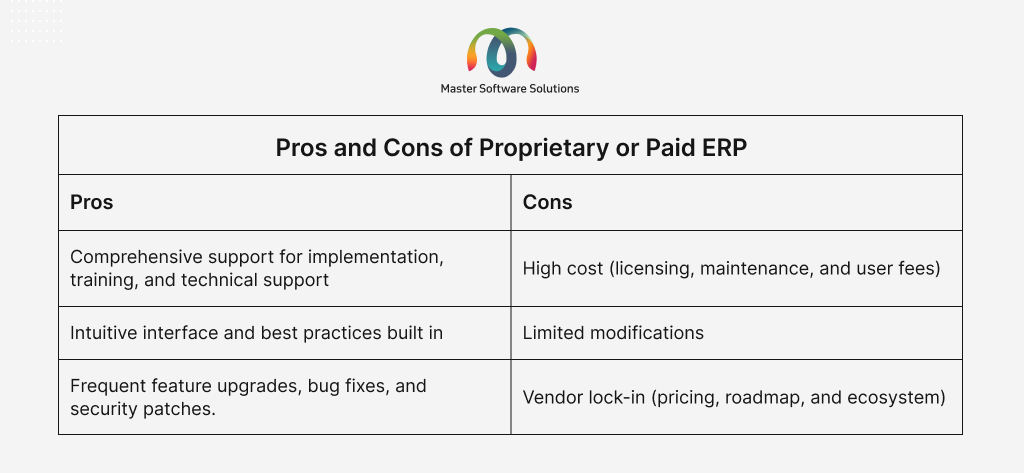
Proprietary or paid ERP
Proprietary ERP systems are commercial software solutions developed by a company and sold under license. Users typically pay a one-time license fee or a subscription fee (SaaS) to use the software and do not have access to the course code. The features of proprietary or paid ERP are:
- They have closed-source, which only vendors can modify.
- It includes support, training, and regular updates.
- These ERPs are feature-rich and polished.
These ERP solutions are suitable for enterprises and mid-sized companies seeking turnkey solutions with minimal IT involvement and robust vendor support. They include SAP S/4HANA, Oracle, NetSuite, Microsoft Dynamics 365, Infor CloudSuite, and Sage X3.
Bottom-line
Selecting the right ERP system isn’t just a technical decision; it is a strategic one that impacts your business’s efficiency, growth, and adaptability. Regardless of the type of ERP system you adopt, the key is to align your ERP selection with your long-term business goals. Understanding these ERP classifications in-depth enables you to assess your needs, ask the right questions, and move confidently in your ERP journey.
Master Software Solutions is an IT service provider that offers ERP consulting services, helping businesses understand various ERP types and suggesting the right system based on their operational pain points. We work with Odoo and Microsoft Dynamics ERP systems to provide tailored solutions that are perfectly suited for businesses. Our ERP consulting services include customizations, integrations, development, and migrations from legacy systems.