After the first and second phases of AI as predictive and generative, now the third phase is here: “autonomous AI agents” that can recommend actions, reason, and handle multi-faceted projects without the need for human supervision. From personal AI assistants in phones to AI agents being used in business operations, AI has revolutionized the way we interact with technology.
However, along with these advancements, there are certain potential risks AI agents pose. These risks and benefits must be considered to help businesses use them effectively while minimizing their downsides. This blog discusses the risks and benefits of AI agents to help you comprehend their full scope and context realistically.
What are AI agents?
AI agents, also known as Agentic AI, are autonomous software that use artificial intelligence and act for users or other systems. They are capable of planning, reasoning, and making decisions to achieve predefined goals. They use Large Language Models (LLMs) to understand and respond to user inputs and determine when to call for an external tool.
Components of AI agents can include sensors for perception or inputs, a decision-making mechanism, actuators for actions, and a learning module for continuous improvement. Examples of AI agents include virtual assistants, fraud detection systems, personalized recommendations, and customer service chatbots.
Six major types of AI agents can help you solve the simplest to the toughest tasks within a matter of seconds. They are:
- Simple reflex agents
- Model-based reflex agents
- Goal-based agents
- Multi-agent systems
- Learning agents
- Utility-based agents
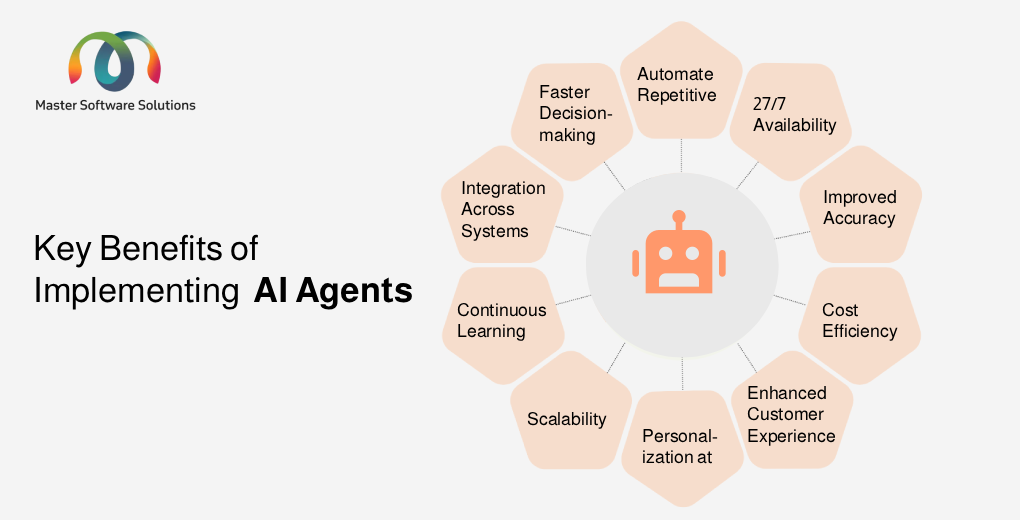
What are the benefits of AI agents?
Building or implementing turnkey AI agent solutions offers numerous advantages, optimizing and streamlining operations while allowing your employees to focus on more strategic tasks. The key benefits of AI agents are:
Automate repetitive tasks
AI agents automate rule-based, time-consuming, and repetitive tasks that don’t need human creativity. This helps reduce the manual workload for employees, minimizes errors in data entry and reporting, and frees up human resources for strategic decision-making. Example: Businesses can implement AI agents to analyze vendor quotes and their previous performance to choose the right one for procurement.
27/7 availability
AI agents never rest, never go on holidays, or get sick, which means they can work continuously, making them valuable in time-sensitive or global operations. This enables round-the-clock customer support, ensures uninterrupted system monitoring and alerting, and supports global teams in different time zones. Example: E-commerce businesses use AI chatbots to answer customer queries, process orders, and track orders at any time of the day.
Improved accuracy and reduced human error
AI agents perform tasks with high precision based on programmed logic and historical data, eliminating human errors. This ensures accuracy in calculations, diagnostics, and predictions, reduces financial risks, and improves compliance and consistency. Example: Businesses use AI agents to predict future customer demands, analyze inventory, and place purchase orders automatically.
Cost efficiency
Though there is an initial setup cost, AI agents can lower operational expenses in the long run. It can automate manual roles and help cut costs, reduce error-related losses and rework, and optimize processes to save time and resources. Example: Businesses use AI agents to detect defects in their products to minimize recalls and wastage.
Faster decision-making
AI agents can process and interpret a large volume of data at speeds far beyond human capability. This helps accelerate business processes like approvals, forecasts, and purchasing, reduces time-to-decision in fast-paced sectors, and enables real-time analytics and responses. Examples: Businesses integrate predictive AI agents to forecast sales, demand, and purchases to be made.
Personalization at scale
AI agents use customer data to tailor experiences to individual preferences at a massive scale, increasing customer engagement and satisfaction. This also improved conversion rates through relevant recommendations and supports marketing automation and targeting. Example: E-commerce businesses use a recommendation AI agent to suggest products based on their search and purchase history.
Scalability
These AI agents can handle thousands of tasks or users simultaneously, which is something that human teams cannot do effectively. It supports business growth without proportionally increasing costs, maintains performance even during spikes in demand, and manages multiple processes in parallel. Example: An AI support bot can handle 10,000 customer queries at once, without hiring a call center team.
Enhanced customer experience
AI agents can quickly address customer needs with context-aware responses, reducing friction. This helps minimize wait times for customers and ensures consistent, polite, and data-backed responses, and proactively helps customers depending on their journey. Example: Television manufacturing businesses use AI agents to help customers troubleshoot issues and book technician visits from a self-service portal.
Integration across systems
AI agents can communicate across various software platforms (ERP, CRM, and POS) to ensure data flow and action coordination. It connects disparate systems to reduce data silos, automate workflow across tools, and centralize visibility into operations. Example: In retail businesses, AI agents fetch customer purchase history from a CRM and suggest restocking items through an ERP system.
Continuous learning
AI agents with machine learning (ML) capabilities improve over time by learning from past decisions, user feedback, and new data. This increases efficiency and accuracy over time, reduces the need for frequent manual reprogramming, and helps adapt to new conditions and user behavior. Examples: Fraud detection AI becomes more accurate as it learns the patterns of legitimate vs. suspicious behavior in banking transactions.
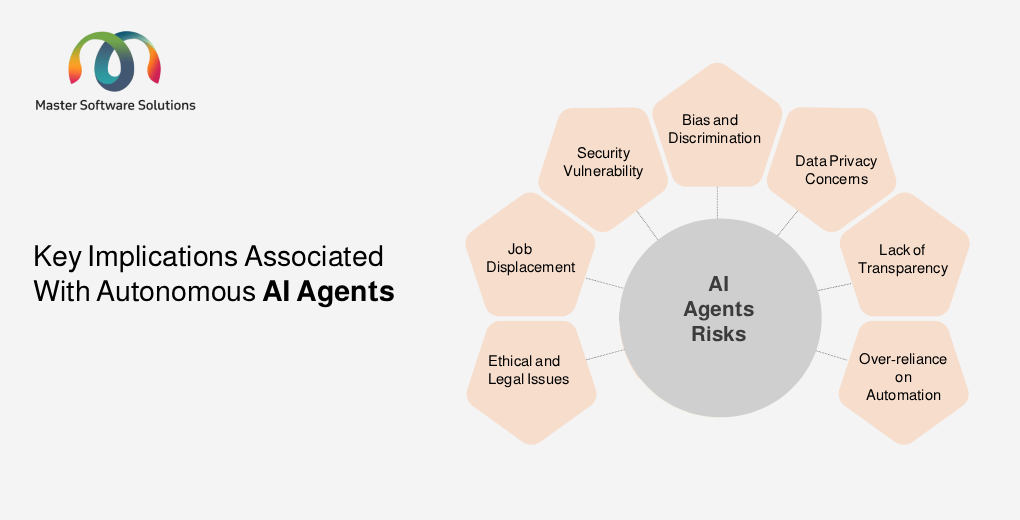
What are the risks of AI agents?
Despite these benefits of AI agents, they pose various risks. Improper AI agent implementation, bias in data, or lack of oversight can lead to serious ethical, operational, and security concerns. Some of the key risks associated with AI agents are:
Bias and discrimination
AI agents learn from historical data, and if that data contains biased or unbalanced information, the AI will reflect and even amplify those biases. Biased hiring algorithms may result in favoring certain genders and ethnicities. AI-based lending systems might discriminate against marginalized communities. Moreover, law enforcement AI might target minority groups based on biased training data.
Data privacy concerns
AI agents often require access to vast amounts of personal or sensitive data to operate effectively. Improper handling of this data can violate privacy rights. This increases the risk of data leaks or cyberattacks, leads to non-compliance with privacy laws like GDPR, and users may lose trust if their data is mishandled.
Lack of transparency
Many AI models, especially complex ones like deep neural networks, do not provide clear reasoning for their decisions, making them a black box. The users and decision makers cannot understand how or why a decision was made, which makes it difficult to detect or fix mistakes and poses legal challenges in regulated industries.
Over-reliance on automation
Businesses may become dependent on AI agents, assuming that they are always correct, or remove human supervision. In critical applications (autonomous vehicles or patient diagnosis), AI errors can have life-threatening consequences. This reduces human accountability and awareness and encourages complacency among human users.
Security vulnerability
AI agents are vulnerable to specialized attacks, such as adversarial inputs or AI model poisoning, which can manipulate their behavior. Hackers can trick AI into making false predictions or taking harmful actions. The sensitive data AI handles can be exposed or stolen. Additionally, poor security practices can compromise entire systems.
Job displacement
AI agents can automate many jobs traditionally performed by humans, especially in customer service, manufacturing, logistics, and data processing. This can lead to mass unemployment in certain sectors. It increases inequality between skilled and unskilled workers.
Ethical and legal issues
AI decisions often impact people’s lives (credit scores, medical treatment, parole decisions). Without human ethics guiding them, these systems may make questionable or harmful decisions. This can result in accountability concerns, unethical decisions without proper oversight, and may violate local or international laws.
Misaligned objectivity
If an AI agent’s goal or performance metric is poorly defined, it may optimize for the wrong outcome or exploit loopholes. This can cause unintended harm or inefficiency. The AI agent can behave unpredictably if its training data doesn’t match real-world needs. It can lead to resource wastage and poor decision-making.
How to deal with these risks?
The World Economic Forum, in collaboration with Capgemini, has presented a white paper that focuses on the AI agent risks and the measures to mitigate them. It promotes
- Establishing ethical guidelines prioritizing human rights, privacy, and accountability, ensuring that AI agent decisions align with human and societal values.
- Emphasizing data governance and cybersecurity before deploying AI agents.
- Implementing public education and awareness strategies that are necessary to mitigate the risk of over-reliance and disempowerment in social interactions with AI agents.
- Facilitating the transparency of agents and incorporating “human-in-loop” management, enabling agents to work autonomously while humans review their decisions after they have made them.
Conclusion
The increasing need for AI agents is more than a technological shift. Understanding the capabilities and limitations of AI agents can help businesses to leverage the full potential of this advanced technology while minimizing associated risks.
Master Software Solutions is an IT service-based company that offers AI agent development services that help businesses build tailored AI agents to streamline processes. We also provide turnkey AI solutions that go beyond traditional automation for various business operations. Hire an AI agent developer to build your custom AI agent tailored for your specific needs.